The Small City Climate Context
- May 14, 2024
- 2 min read
Updated: Jul 8, 2025
Cities are both culprits and casualties in the climate crisis. But what about the ones we rarely hear about? In Nāgrika’s Climate Change Series, Part 1 zooms in on India’s small and midsized cities, revealing overlooked risks, urgent gaps in data, and why ignoring them could mean missing the bigger climate picture entirely.
Summary & Key Insights

Causes and Impacts of Climate Change:
Human activities, particularly since modern industrialisation, have accelerated greenhouse gas emissions. While natural causes also influence the climate, burning of fossil fuels and deforestation have increased such emissions in the atmosphere.
The increased concentration of greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, has led to an intensifying greenhouse effect, which has contributed to accelerated global warming. It is observed that these gases absorb almost 90% of the heat radiated by the earth’s surface in the form of infrared and then re-radiate it, thereby slowing the process of heat loss to space.
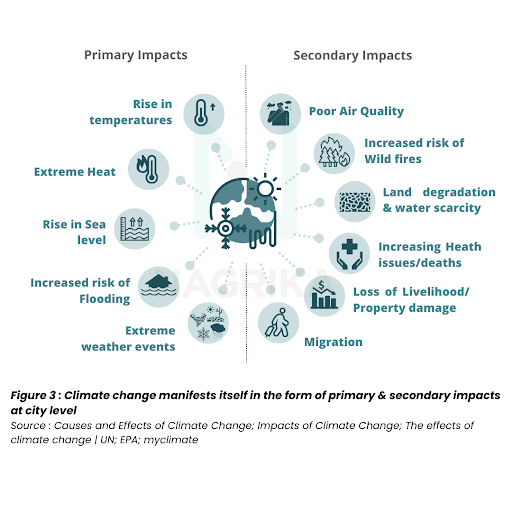
While poor air quality, extreme heat, sea level rise, increased flooding risks, and more frequent extreme weather events are primary impacts, secondary impacts include land degradation, wildfires, biodiversity loss, rising health issues, migration, and loss of livelihoods.
The dual role of Cities as Contributors and Sufferers:
Rural areas also contribute to the current rate of climate change, but several studies indicate that it is the urban areas that are the highest contributors. City systems have been identified as one of the key systems that are responsible for about 90% of global GHG emissions.
A 2018 study covering around 13,000 cities globally observed that just 100 cities (out of which 19 were small and mid-sized) drive 18% of the emissions.
Within the city system, several sectors emit GHGs; however, it is the energy sector that accounts for over three-quarters of the emissions.
Simultaneously, cities are also among the worst sufferers, experiencing adverse impacts and disasters induced by climate change. As per a report in 2022, out of 998 cities worldwide, approximately 80% reported experiencing at least one climate-related disaster.
Vulnerability of Indian Cities:
According to a 2021 study, 99 of the 100 most vulnerable cities in the world were in Asia, with India having 43 on this list.
India is also home to 13 of the world’s riskiest cities, which also include small and midsized cities like Agra.
Even though India’s overall emissions are lower than the global average, India’s urban centres are responsible for nearly 44% of carbon emissions. This is due to a heavy reliance on meeting energy demands through coal, oil, and solid biomass.
In 2023, Indian cities experienced extreme weather events on 318 days out of 365 days, which also resulted in 3,287 deaths. This highlights the urgent need for cities to prepare for disasters and strengthen their infrastructure to withstand growing climate extremes.
Comments